Use K Nearest Neighbor (KNN) for a better Company.
Adam Louly
—May 08, 2018
Use K Nearest Neighbor (KNN) for a better Company.

Introduction
Most of companies problems are resignation’s of salaries, one of the major cause of resignations that they are not comfort on the place that they are working in, either the team they are working with, or the employees that they are having there offices in the same department, an idea comes in mind why not classifying people using KNN, so we can get the best place to work for our salaries, How is that ? in this article I will clarify how this classification is working.
We’ll see how can we use K Nearest Neighbor Algorithm to help us in this labour-intensive task.
Here’s a general overview of what we will do:
Getting a data set about relationships between people with different characteristics .
Calculating distances between 2 salaries depending on a table of distances that is generated from the training data set.
Use the classifier to classify a new salary into the right department.
The data
First of all, we’re going to need a data set. For that I have suggested to get it from relationships between people with different characteristics ,this data can be extracted from anywhere , social media ,court cases etc ..— this data set is a collection of data like (interests , gender , family situation , religion , roots , personal details etc .. ).
How to calculate the DISTANCE
We are going to use a table that have distances based on comprehension between two features on the salaries, this table will have 0 in the diagonal since 2 employees whom having the same feature are close, these values are changeable from time to another, and extracted from real life actions, like if racism is high in a country A against country B, the distance between a salary from A and another from B will be long.
The sum of distances will be used instead of Euclidean distance in the KNN.
For example:
Let’s say we have a company of 3 salaries and 3 offices. We want to recruit in three more salaries, provided that each employee will enter an office. In the end, we will get 6 salaries at the company, at the rate of two employees in each office. We will use the method I explained earlier to get new salaries into the office that will suit them.
List of salaries :
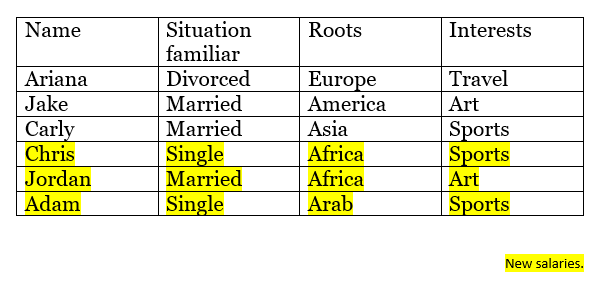
Table of distances:
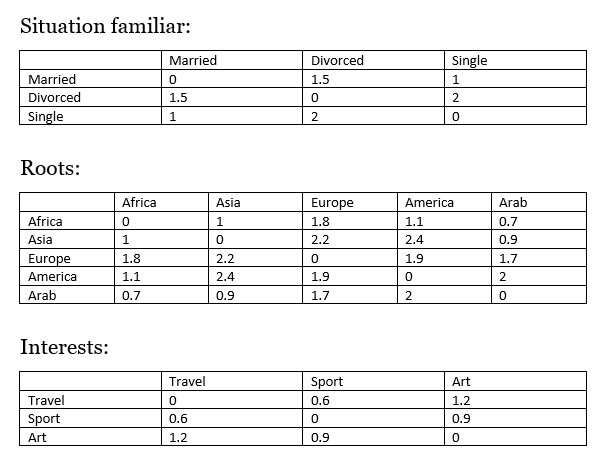
Note : The numbers on the tables are random numbers , they are not based on anything.
In this example we are taking 3 attributes to calculate distance , familiar situation, roots and interests .
Note : you should use many attributes in order to get good results.
This is the state 1 of the company:
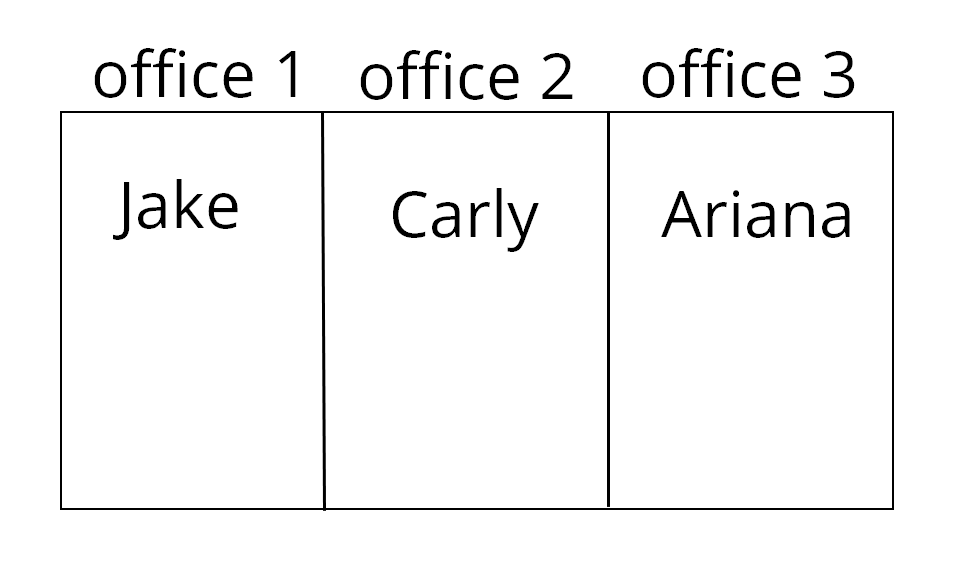
We will classify the 3 new salaries whom are: Chris, Jordan and Adam.
We need to put each employee on each office, so we need to calculate the distance between each new salary and each old salary.
Calculating the distances :
For Chris:
D(Chris,Jake) =D(Single,Married)+D(Africa,America)+D(Sports,Art)
=1+1.1+0.9=3
D(Chris,Carly) =D(Single,Married)+D(Africa,Asia)+D(Sports,Sports)
=1+1+0=2
D(Chris,Ariana) =D(Single,Divorced)+D(Africa,Europe)+D(Sports,Travel)
=2+1.8+0.6=4.4
For Jordan:
D(Jordan,Jake) =D(Married,Married)+D(Africa,America)+D(Art,Art)
=0+1.1+0=1.1
D(Jordan,Carly) = D(Married,Married)+D(Africa,Asia)+D(Art,Sports)
=0+1+0.9=1.9
D(Jordan,Ariana) = D(Married,Divorced)+D(Africa,Europe)+D(Art,Travel)
=1.5+1.8+1.2=4.5
For Adam:
D(Adam,Jake) = D(Single,Married)+D(Arab,America)+D(Sports,Art)
=1+2+0.9=3.9
D(Adam,Carly) = D(Single,Married)+D(Arab,Asia)+D(Sports,Sports)
=1+0.9+0=1.9
D(Adam,Ariana) = D(Single,Divorced)+D(Arab,Asia)+D(Sports,Sports)
=1.5+0.9+0=2.4
Now after calculating the distances based on the figure 2 , we get this:
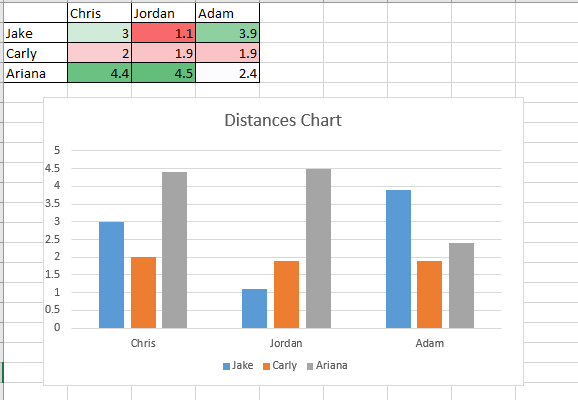
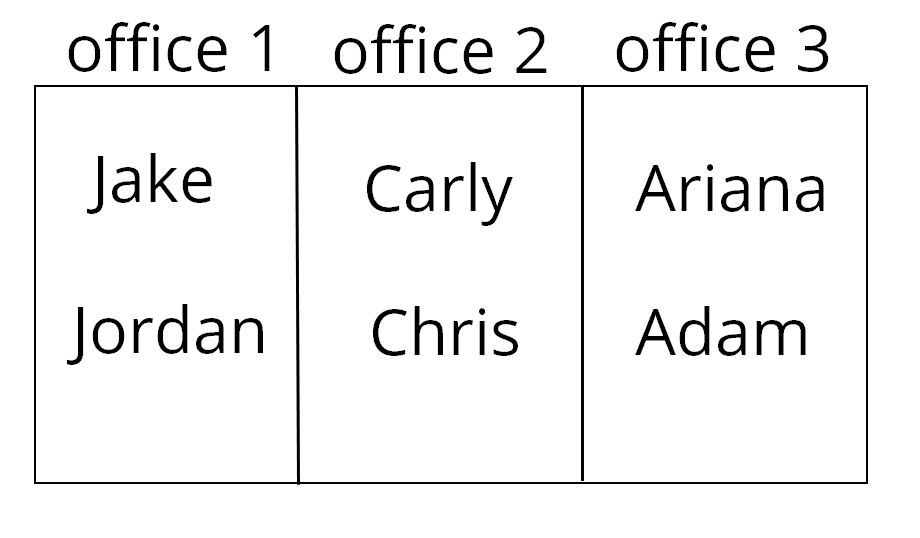
From the table and the chart we can classify the 3 new employees this way:
Chris will be in the office number 2 with Carly.
Jordan will be in the office number 1 with Jake.
Adam will be in the office number 3 with Ariana.
The K = 1 In this case, since we only have 1 salary on each office, the K ratio is changeable from case to case depends on how large the company is.

Conclusion :
We were able to avoid the random classification of new salaries in a company , we are now having something to be based on when a new salary comes into a company and we want to put it on the right ecosystem for a better productivity from the employees , and less conflicts in the company.